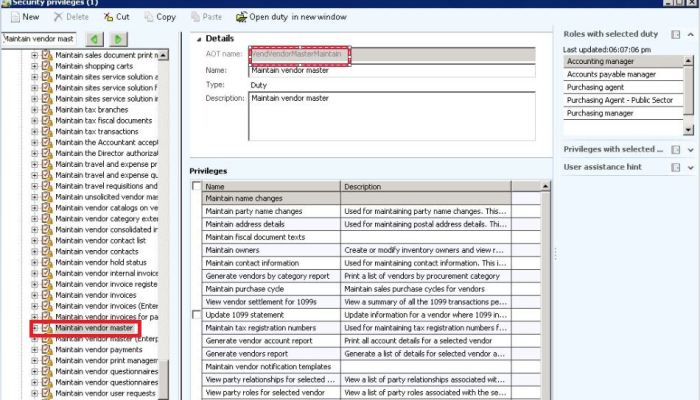
Overview
There are multiple methods to develop SSRS reports in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012. This tutorial will guide you in developing Report Data Provider (RDP) based SSRS reports.RDP based SSRS Reports are used when complex business logic cannot be achieved using AOT query.
Pre-requisites
- Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012
- Visual studio 2012
- SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) must be configured
- Reporting services extensions must be installed in Dynamics AX
Important Concepts
-
Report Data Provider (RDP) Class
Report Data Provider Class is an X++ class that is used to access and
process data for a SSRS report. The RDP class processes the business
logic based on a specified parameter and/or query and returns a dataset
to the reporting services. In order to create a RDP class in AX, you
have to extend that class with SRSReportDataProviderBase. This tells AX that this class will be used by reporting services to process the data. - SRSReportQueryAttribute: specifies which AOT query will be used in this report. If the RDP class uses an AOT query to process data, define this attribute at the beginning of the class.
- SRSReportParameterAttribute: defines the data contract class that will be used by this report to prompt for parameter values. If the RDP class contains any parameters this define this attribute at the beginning of the class.
-
Data Contract Class
A data contract class is an X++ class which contains parm methods with the DataMemberAttribute defined at the beginning of the method. This class is used to define one or more parameters that will be used in a SSRS report. -
Table
Two important attributes are used in RDP classes:
An AX table is used as the dataset to
store data for the report. The RDP class processes the data and stores
it in the table which is then used by a SSRS report to render data.
A table can be a temporary table (InMemory or TempDB) or a regular table, but it is Microsoft best practice to use a temporary table.
The type of temporary table is based upon the performance considerations. InMemory temporary table is used when the data set is small, while TempDB is normally used for larger datasets to improve performance.
Scenario
As part of this tutorial, the report will print a list of customers and their invoiced sales order counts.Steps
- First of all, create a temporary table. Open AOT à Date Dictionary à Tables.
- Right Click on Tables and create a new Table called CustReportRDPDemoTmp.
- Set the TableType property to InMemory. This will define the table as a temporary table.
- Expand the CustReportRDPDemoTmp table node and add the following fields in the table:
- The final table should look like the following:
- Now create a RDP class. Go to Classes and create a new class called CustReportRDPDemoDP by right clicking on Classes and selecting New Class. It is a best practice to suffix the RDP class name with DP .
- Open the Class declaration by right clicking on it and selecting View code.
- Now write the following code:
- Add a new method and name it getCustReportRDPDemoTmp. This method is mandatory because reporting services uses this method to get the table buffer containing the processed data. The SRSReportDataSetAttribute attribute is used to indicate the temporary table name and also tells the reporting services to use this method to retrieve the processed data.
- Write the following code in the method:
- Add a new method and name it processReport. This method contains the business logic and is called by reporting services to generate data.
- This method will query customer details and fill the temporary table buffer. Write the following code in the method:
- Now create a new report. Since the development of a SSRS report is done in Visual studio, we first need to create a new project in Visual studio.
- Open Visual studio. Go to File à New à Project
- In the Installed templates section select Microsoft Dynamics AX and then select Report Model in the right pane. Name the project RDPBasedDemo and press Ok.
- A new project will be created as shown below.
- Now add a new report in the project by right clicking on the project RDPBasedDemo à Add à Report.
- A report will be added to the project with the name Report1. Rename the report RDPBasedDemo.
- Now double click the report to open it.
- The description of the individual node is given below:
- Datasets: Datasets retrieve data from RDP class. It acts as a bridge between AX and the SSRS report. Only the fields added in the datasets can be used in a report.
- Designs: It defines the layout of the report.
- Images: It contains the images that you want to display in the SSRS report.
- Data Methods: It contains the business logic which can then be used in the report.
- Parameters: It is used to apply filtering to the data in a report. All the parameters defined in the data contract class are automatically added here when the RDP class is defined in the datasets.
- Now you will want to create a new Dataset by right clicking Datasets àAdd Dataset. Name it CustDetail.
- Select the CustDetail dataset and open the properties window. Set the Data Source Type to Report Data Provider. Then select the Query field. An ellipse button appears. Click it to open a dialog box.
- This dialog box lists all the RDP classes present in the AOT. Select CustReportRDPDemoDP and press Next.
- Select the fields to be displayed in the report and press OK. Only the fields selected in this dialog box can be shown in the report.
- There are two types of designs that can be created in a SSRS report:
- Auto design: Visual studio automatically creates a design based on the dataset provided. Auto design is the preferred method because it is easy and usually fulfills the majority scenarios.
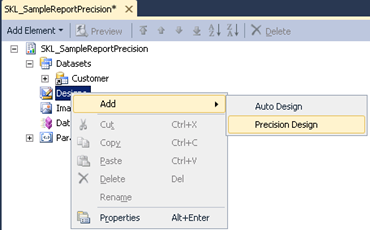
- Precision Design: This is used when you need custom placement of fields or the layout of the report is too complex.
- In this demo we will use Auto Design. Now right click the Designs nodeàAdd àAuto Design. A new design is added. Rename it Design. It is recommended that you set the name of the Design to either ‘Design‘ or ‘Report‘.
- Now drag the CustDetail form to the Datasets node and drop it on the Design node. A table will be created which contain all the fields present in the data set. These fields will appear in the same order as in the report. So if you want to arrange the fields, right click the field and select either ‘move up’ or ‘move down’.
- The final design should look like the following:
- Now we have to define the layout of the report. Visual studio provides built in templates. Select the Design and open the properties window. Select ReportLayoutStyleTemplate in the LayoutTemplate field. Give a suitable title to the report.
- Select CustDetailTable under the Design node and open the properties window. Select TableStyleAlternatingRowsTemplate in the Style Template field.
- The report is now completed and can be viewed. To preview the report, select the Design node, right click it and select preview.
- Select the Report tab. The report will appear as shown below:
- To view this report from AX, Add the report to AOT and create an Output menu item and set the appropriate Properties. For further details on creating SSRS reporting, refer to our previous article ‘Developing SSRS report using Query‘.


| S. No. | Field name | Extended Data Type | Label |
| 1 | CustAccount | CustAccount | |
| 2 | Name | Name | |
| 3 | SalesOrderInvoiceCount | Integer | Sales order invoiced |